How to set up port forwarding in Mikrotik

The article content
Let's take a little more detail, using the example of the MikroTik RB951-2nb router - it has 5 ports, plus a WiFi module.
In MikroTik, the management of port forwarding settings is located in the IP =Firewall =NAT menu.
By default, the same masquerading is registered here - the substitution of internal local addresses with an external server address. We will create an additional port forwarding rule here.
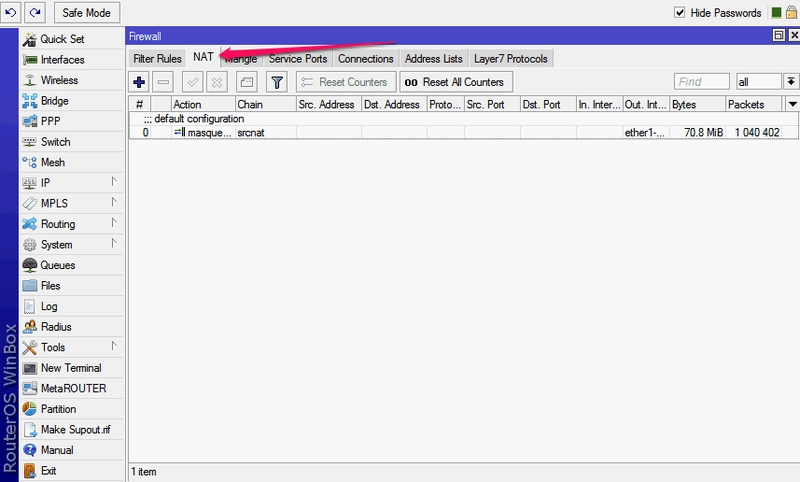
SETTING UP THE GENERAL TAB
Click the plus sign and fill in several fields in the window that appears:
- Chain- the direction of the data flow. In the selection list - srcnat, which means "from the inside out", i.e. from the local network to the outside world, anddstnat - from the external network to the internal. We choose the latter, since we will accept incoming connections.
- Src. Address Dst. Address- the external address from which the connection will be initiated, and the destination address (always the router address). We leave it blank.
- Protocol- here we specify the type of protocol for our connection, tcp or udp, we fill it in necessarily.
- Src. Port(outgoing port) - the port of the remote computer from which the data will be sent, we leave empty if it does not matter to us.
- Dst. Port (destination port) - we put down the number of the external port of the router, to which data from the remote machine will come and be forwarded to our computer on the internal network.
- Any. Port(any port) - if we put the port number here, we will indicate to the router that this port will be used both as outgoing and incoming (combining the two previous fields in one).
- In. interface (incoming interface) - here we specify the interface of the MikroTik router on which it is used, "listens" this port. In our case, since we are doing a forwarding to receive data from the outside, this is the interface through which the router is connected to the Internet, by default this is the ether1-gateway. The parameter must be specified, otherwise the port will not be accessible from the local network. If we are connected to the provider via pppoe, then it may be necessary to specify it, and not the WAN interface.
- Out. interface (outgoing interface) - the connection interface of the computer for which we are doing port forwarding.
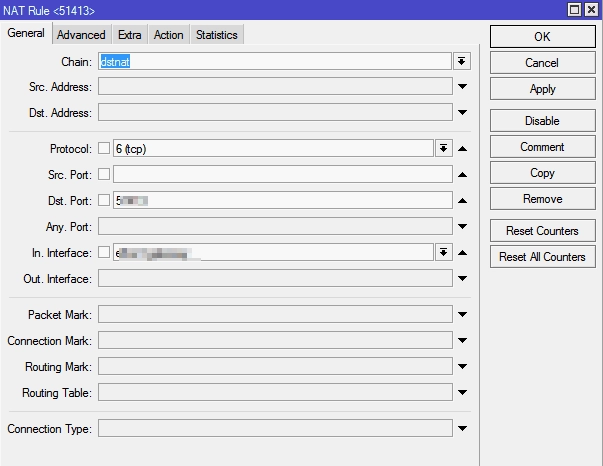
SETTING UP THE ACTION TAB
In the Action field, we prescribe the action that the router will have to perform. Options are offered:
- accept — just accepts data;
- add-dst-to-address-list the destination address is added to the address list;
- add-src-to-address-list the outgoing address is added to the corresponding address list;
- dst-nat — redirects data from the external network to the local, internal (select this option);
- jump allows the rule to be applied from another channel, for example, when the Chain value is set to srcnat, apply the rule todstnat;
- log — just writes information about the data to the log;
- masquerade masquerading: substitution of the internal address of a computer or other device from a local network to the address of a router;
- netmap creates redirection of one set of addresses to another, acts more extensively than dst-nat;
- passthrough — this rule setting item is skipped and the transition immediately takes place to the next one. Used for statistics;
- redirect data is redirected to another port of the same router;
- return — if we got into this channel by the jump rule, then this rule brings us back;
- same — rarely used setting of the same rules for a group of addresses;
- src-nat forwarding packets from the internal network to the external network (reverse dst-nat redirection).
The dst-nat and netmap options are suitable for our settings. Choose dst-nat.
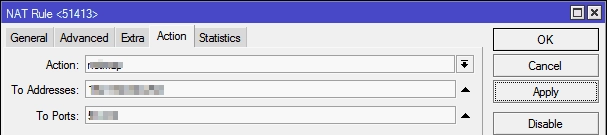
In the fieldTo Addresses, we write the internal IP address of the computer or device to which the router will have to forward data according to the port forwarding rule.
In the fieldTo Ports, respectively, the port number, for example:
- 80/tcp— WEB server,
- 22/tcp — SSH,
- 1433/tcp — MS SQL Server,
- 161/udp — snmp,
- 23/tcp — telnet and so on.
If the values in the field areDst. Port of the previous tab and in the field To Ports are the same, then you can not specify it here.
Next, we add a comment to the rule to remember why we created it.
Thus, we have created a rule for port forwarding and access to the internal computer (on the local network) from the Internet. Recall that it needs to be put above the standard masquerading rules, otherwise it will not work (Microtik polls the rules sequentially).